25AA640/25LC640/25C640
3.3
Write Sequence
3.0
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Prior to any attempt to write data to the 25xx640 array
or status register, the write enable latch must be set by
issuing the WREN instruction (Figure 3-4). This is
done by setting CS low and then clocking out the
proper instruction into the 25xx640. After all eight bits
of the instruction are transmitted, the CS must be
brought high to set the write enable latch. If the write
operation is initiated immediately after the WREN
instruction without CS being brought high, the data will
not be written to the array because the write enable
latch will not have been properly set.
3.1
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
The 25xx640 is a 8192 byte Serial EEPROM designed
to interface directly with the Serial Peripheral Interface
(SPI) port of many of today’s popular microcontroller
families, including Microchip’s PIC16C6X/7X micro-
controllers. It may also interface with microcontrollers
that do not have a built-in SPI port by using discrete
I/O lines programmed properly with the software.
The 25xx640 contains an 8-bit instruction register. The
part is accessed via the SI pin, with data being clocked
in on the rising edge of SCK. The CS pin must be low
and the HOLD pin must be high for the entire opera-
tion.
Once the write enable latch is set, the user may pro-
ceed by setting the CS low, issuing a write instruction,
followed by the address, and then the data to be writ-
ten. Up to 32 bytes of data can be sent to the 25xx640
before a write cycle is necessary.The only restriction is
that all of the bytes must reside in the same page. A
page address begins with XXX0 0000 and ends with
XXX1 1111. If the internal address counter reaches
XXX1 1111 and the clock continues, the counter will
roll back to the first address of the page and overwrite
any data in the page that may have been written.
Table 3-1 contains a list of the possible instruction
bytes and format for device operation. All instructions,
addresses, and data are transferred MSB first, LSB
last.
Data is sampled on the first rising edge of SCK after
CS goes low. If the clock line is shared with other
peripheral devices on the SPI bus, the user can assert
the HOLD input and place the 25xx640 in ‘HOLD’
mode. After releasing the HOLD pin, operation will
resume from the point when the HOLD was asserted.
For the data to be actually written to the array, the CS
must be brought high after the least significant bit (D0)
th
of the n data byte has been clocked in. If CS is
brought high at any other time, the write operation will
not be completed. Refer to Figure 3-2 and Figure 3-3
for more detailed illustrations on the byte write
sequence and the page write sequence respectively.
While the write is in progress, the status register may
be read to check the status of the WPEN, WIP, WEL,
BP1, and BP0 bits (Figure 3-6). A read attempt of a
memory array location will not be possible during a
write cycle. When the write cycle is completed, the
write enable latch is reset.
3.2
Read Sequence
The part is selected by pulling CS low. The 8-bit read
instruction is transmitted to the 25xx640 followed by the
16-bit address with the three MSB’s of the address
being don’t care bits. After the correct read instruction
and address are sent, the data stored in the memory at
the selected address is shifted out on the SO pin. The
data stored in the memory at the next address can be
read sequentially by continuing to provide clock pulses.
The internal address pointer is automatically incre-
mented to the next higher address after each byte of
data is shifted out. When the highest address is
reached (1FFFh), the address counter rolls over to
address 0000h allowing the read cycle to be continued
indefinitely. The read operation is terminated by raising
the CS pin (Figure 3-1).
TABLE 3-1:
INSTRUCTION SET
Instruction Name
Instruction Format
Description
READ
WRITE
WREN
WRDI
0000 0011
0000 0010
0000 0110
0000 0100
0000 0101
0000 0001
Read data from memory array beginning at selected address
Write data to memory array beginning at selected address
Set the write enable latch (enable write operations)
Reset the write enable latch (disable write operations)
Read status register
RDSR
WRSR
Write status register
DS21223A-page 6
Preliminary
1997 Microchip Technology Inc.






 STM32F030C6芯片介绍:主要参数分析、引脚配置说明、功耗及封装
STM32F030C6芯片介绍:主要参数分析、引脚配置说明、功耗及封装

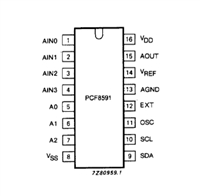 PCF8591数据手册解读:参数、引脚说明
PCF8591数据手册解读:参数、引脚说明

 一文带你了解ss8050参数、引脚配置、应用指南
一文带你了解ss8050参数、引脚配置、应用指南

 深入解析AD7606高性能多通道模数转换器:资料手册参数分析
深入解析AD7606高性能多通道模数转换器:资料手册参数分析
