X1243
Section 5) is a volatile register. It is not necessary to set the
RWEL bit prior to writing the status register. Section 5)
supports a single byte read or write only. Continued reads or
writes from this section terminates the operation.
Writing to the Real Time Clock
The time and date may be set by writing to the RTC
registers. To avoid changing the current time by an
uncompleted write operation, the current time value is
loaded into a separate buffer at the falling edge of the clock
on the ACK bit before the RTC data input bytes, the clock
continues to run. The new serial input data replaces the
values in the buffer. This new RTC value is loaded back into
the RTC Register by a stop bit at the end of a valid write
sequence. An invalid write operation aborts the time update
procedure and the contents of the buffer are discarded. After
a valid write operation the RTC will reect the newly loaded
data beginning with the rst “one second” clock cycle after the
stop bit. The RTC continues to update the time while an RTC
register write is in progress and the RTC continues to run
during any nonvolatile write sequences. A single byte may
be written to the RTC without affect-ing the other bytes.
The state of the CCR can be read by performing a ran-dom
read at any address in the CCR at any time. This returns the
contents of that register location. Additional registers are
read by performing a sequential read. The read instruction
latches all Clock registers into a buffer, so an update of the
clock does not change the time being read. A sequential
read of the CCR will not result in the output of data from the
memory array. At the end of a read, the master supplies a
stop condition to end the operation and free the bus. After a
read of the CCR, the address remains at the previous
address +1 so the user can execute a current address read
of the CCR and continue reading the next Register.
Alarm Registers
Clock/Control Registers (CCR)
There are two alarm registers whose contents mimic the
contents of the RTC register, but add enable bits and
exclude the 24-hour time selection bit. The enable bits
specify which registers to use in the comparison between the
Alarm and Real Time Registers. For example:
The Control/Clock Registers are located in an area log-ically
separated from the array and are only accessible following a
slave byte of “1101111x” and reads or writes to addresses
[0000h:003Fh].
CCR Access
- The user can set the X1242 to alarm every Wednes-day
at 8:00AM by setting the EDWn, the EHRn and EMNn
enable bits to ‘0’ and setting the DWAn, HRAn and
MNAn Alarm registers to 8:00AM Wednesday.
- A daily alarm for 9:30PM results when the EHRn and
EMNn enable bits are set to ‘0’ and the HRAn and
MNAn registers set 9:30PM.
- Setting the EMOn bit in combination with other enable
bits and a specic alarm time, the user can establish an
alarm that triggers at the same time once a year.
When there is a match, an alarm ag is set. The occur-rence
of an alarm can be determined by polling the AL0 and AL1
bits, or by setting the AL0E and AL1E bits to ‘1’ and
monitoring the IRQ output. The AL0E and AL1E bits enable
the circuit that triggers the output IRQ pin when an alarm
occurs. Writing a ‘0’ to one of the bits disables the output
IRQ for that alarm condition, The alarm enable bits are
located in the MSB of the but the alarm condition can still be
checked by polling particular register. When all enable bits
are set to ‘0’, the alarm ag. there are no alarms.
The contents of the CCR can be modied by performing a
byte or a page write operation directly to any address in the
CCR. Prior to writing to the CCR (except the status register),
however, the WEL and RWEL bits must be set using a two
step process (See section “Writing to the Clock/Control
Registers.”)
The CCR is divided into 5 sections.These are:
1. Alarm 0 (8 bytes)
2. Alarm 1 (8 bytes)
3. Control (2 bytes)
4. Real Time Clock (8 bytes)
5. Status (1 byte)
Sections 1) through 3) are nonvolatile and Sections 4) and 5)
are volatile. Each register is read and written through
buffers. The nonvolatile portion (or the counter portion of the
RTC) is updated only if RWEL is set and only after a valid
write operation and stop bit. A sequential read or page write
operation provides access to the contents of only one
section of the CCR per operation. Access to another section
requires a new operation. Continued reads or writes, once
reaching the end of a section, will wrap around to the start of
the section. A read or page write can begin at any address in
the CCR.
FN8249.0
3
April 28, 2005






 STM32F030C6芯片介绍:主要参数分析、引脚配置说明、功耗及封装
STM32F030C6芯片介绍:主要参数分析、引脚配置说明、功耗及封装

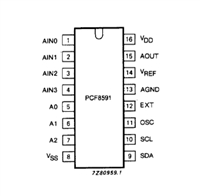 PCF8591数据手册解读:参数、引脚说明
PCF8591数据手册解读:参数、引脚说明

 一文带你了解ss8050参数、引脚配置、应用指南
一文带你了解ss8050参数、引脚配置、应用指南

 深入解析AD7606高性能多通道模数转换器:资料手册参数分析
深入解析AD7606高性能多通道模数转换器:资料手册参数分析
