ADP3416
THEORY OF OPERATION
SW Pin to reach 1 V, the overlap protection circuit ensures that
Q1 is OFF before Q2 turns on, regardless of variations in tem-
perature, supply voltage, gate charge, and drive current.
The ADP3416 is a dual MOSFET driver optimized for driving
two N-channel MOSFETs in a synchronous buck converter
topology. A single PWM input signal is all that is required to
properly drive the high side and the low side FETs. Each driver
is capable of driving a 3 nF load.
To prevent the overlap of the gate drives during Q2’s turn OFF
and Q1’s turn ON, the overlap circuit provides a internal delay
that is set to 50 ns. When the PWM input signal goes high, Q2
will begin to turn OFF (after a propagation delay), but before
Q1 can turn ON, the overlap protection circuit waits for the
voltage at DRVL to drop to around 10% of VCC. Once the
voltage at DRVL has reached the 10% point, the overlap protec-
tion circuit will wait for a 20 ns typical propagation delay. Once
the delay period has expired, Q1 will begin turn ON.
A more detailed description of the ADP3416 and its features
follows. Refer to the Functional Block Diagram.
Low Side Driver
The low side driver is designed to drive low RDS(ON) N-channel
MOSFETs. The maximum output resistance for the driver is
4 Ω for sourcing and 2.5 Ω for sinking gate current. The low
output resistance allows the driver to have 40 ns rise and
30 ns fall times into a 3 nF load. The bias to the low side driver
is internally connected to the VCC supply and PGND.
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Supply Capacitor Selection
For the supply input (VCC) of the ADP3416, a local bypass
capacitor is recommended to reduce the noise and to supply some
of the peak currents drawn. Use a 1 µF, low ESR capacitor.
Multilayer ceramic chip (MLCC) capacitors provide the best
combination of low ESR and small size and can be obtained from
the following vendors:
When the driver is enabled, the driver’s output is 180 degrees
out of phase with the PWM input. When the ADP3416 is dis-
abled, the low side gate is held low.
High Side Driver
The high side driver is designed to drive a floating low RDS(ON)
N-channel MOSFET. The maximum output resistance for the
driver is 4 Ω for sourcing and 2.5 Ω for sinking gate current.
The low output resistance allows the driver to have 40 ns rise
and 30 ns fall times into a 3 nF load. The bias voltage for the
high side driver is developed by an external bootstrap supply
circuit, which is connected between the BST and SW Pins.
Murata GRM235Y5V106Z16 www.murata.com
Taiyo-
Yuden
Tokin
EMK325F106ZF
C23Y5V1C106ZP
www.t-yuden.com
www.tokin.com
Keep the ceramic capacitor as close as possible to the ADP3416.
The bootstrap circuit comprises a diode, D1, and bootstrap
capacitor, CBST. When the ADP3416 is starting up, the SW Pin
is at ground, so the bootstrap capacitor will charge up to VCC
through D1. When the PWM input goes high, the high side
driver will begin to turn the high side MOSFET, Q1, ON by
pulling charge out of CBST. As Q1 turns ON, the SW Pin will
rise up to VIN, forcing the BST Pin to VIN + VC(BST), which is
enough gate to source voltage to hold Q1 ON. To complete the
cycle, Q1 is switched OFF by pulling the gate down to the volt-
age at the SW Pin. When the low side MOSFET, Q2, turns
ON, the SW Pin is pulled to ground. This allows the bootstrap
capacitor to charge up to VCC again.
Bootstrap Circuit
The bootstrap circuit uses a charge storage capacitor (CBST) and a
Schottky diode, as shown in Figure 1. Selection of these compo-
nents can be done after the high side MOSFET has been chosen.
The bootstrap capacitor must have a voltage rating that is able
to handle the maximum battery voltage plus 5 volts. A minimum
50 V rating is recommended. The capacitance is determined
using the following equation:
QGATE
∆VBST
CBST
=
The high side driver’s output is in phase with the PWM input.
When the driver is disabled, the high side gate is held low.
where, QGATE is the total gate charge of the high side MOSFET,
and ∆VBST is the voltage droop allowed on the high side MOSFET
drive. For example, the IRF7811 has a total gate charge of about
20 nC. For an allowed droop of 200 mV, the required boot-
strap capacitance is 100 nF. A good quality ceramic capacitor
should be used.
Overlap Protection Circuit
The overlap protection circuit (OPC) prevents both of the main
power switches, Q1 and Q2, from being ON at the same time.
This is done to prevent shoot-through currents from flowing
through both power switches and the associated losses that can
occur during their ON-OFF transitions. The overlap protection
circuit accomplishes this by adaptively controlling the delay from
Q1’s turn OFF to Q2’s turn ON, and by internally setting the
delay from Q2’s turn OFF to Q1’s turn ON.
A Schottky diode is recommended for the bootstrap diode due
to its low forward drop, which maximizes the drive available for
the high side MOSFET. The bootstrap diode must have a mini-
mum 40 V rating to withstand the maximum battery voltage
plus 5 V. The average forward current can be estimated by:
To prevent the overlap of the gate drives during Q1’s turn OFF
and Q2’s turn ON, the overlap circuit monitors the voltage at the
SW Pin. When the PWM input signal goes low, Q1 will begin to
turn OFF (after a propagation delay), but before Q2 can turn ON,
the overlap protection circuit waits for the voltage at the SW Pin
to fall from VIN to 1 V. Once the voltage on the SW Pin has fallen
to 1 V, Q2 will begin turn ON. By waiting for the voltage on the
IF(AVG) ≈ QGATE × fMAX
where fMAX is the maximum switching frequency of the control-
ler. The peak surge current rating should be checked in-circuit,
since this is dependent on the source impedance of the 5 V
supply, and the ESR of CBST
.
–6–
REV. A






 STM32F030C6芯片介绍:主要参数分析、引脚配置说明、功耗及封装
STM32F030C6芯片介绍:主要参数分析、引脚配置说明、功耗及封装

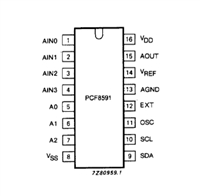 PCF8591数据手册解读:参数、引脚说明
PCF8591数据手册解读:参数、引脚说明

 一文带你了解ss8050参数、引脚配置、应用指南
一文带你了解ss8050参数、引脚配置、应用指南

 深入解析AD7606高性能多通道模数转换器:资料手册参数分析
深入解析AD7606高性能多通道模数转换器:资料手册参数分析
